
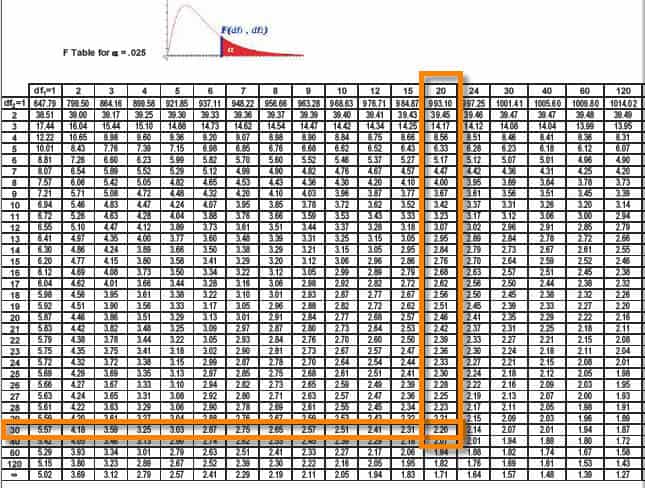
It is used to test the hypothesis that the means of given normally distributed populations with the same standard deviation are equal. The F-Test is used to test the hypothesis that the variances of two populations are equal. One can use the F-Test formula in a wide variety of settings: Step 5: Since the F statistic (1.55) is lesser than the table value obtained (2.348), we cannot reject the null hypothesis. The F value from the F Table with degrees of freedom as 10 and 20 is 2.348. Step 4: Since it is a two-tailed test, alpha level = 0.10/2 = 0.05. Step 1: Null Hypothesis H 0: σ 1 2 = σ 2 2. Carry out a two-tailed F-test with a level of significance of 10%. The sample size for the Delhi head office is 11, and that for the Mumbai branch is 21. The variance of Delhi head office customers is 31, and that for the Mumbai branch is 20. He carries out a research study of customers. The Operations Manager of the bank wonders if the customers at one branch are more variable than the number of customers at another. There are long customer queues at one office, while customer queues are short at the other. 
The bank has a head office in Delhi and a branch in Mumbai.
Step 5: Since F statistic (4) is more than the table value obtained (2.026), we reject the null hypothesis. The F value from the F Table with degrees of freedom as 10 and 50 is 2.026. Step 4: Since it is a two-tailed test, alpha level = 0.10/2 = 0.050. If the F statistic obtained in Step 2 is less than the critical value at the required significance level, we cannot reject the null hypothesis. We reject the null hypothesis if the F statistic exceeds the critical value at the required significance level. Compare the F statistic obtained in Step 2 with the critical value obtained in Step 4. Note: There are different F Tables for different levels of significance. Thus, the F-value is found by looking at the degrees of freedom in the numerator and the denominator in the F-table. i.e., = σ 1 2 / σ 2 2 Where σ 1 2 is assumed to be larger sample variance, and σ 2 2 is the smaller sample varianceĭegree of freedom (df1) = n1 – 1 and Degree of freedom (df2) = n2 – 1 where n1 and n2 are the sample sizes.įor two-tailed tests, divide the alpha by 2 to find the correct critical value. Here, σ 1 2 and σ 2 2 are the symbols for variances. The alternate hypothesis states that the variances are unequal. The null hypothesis assumes that the variances are equal. Firstly, frame the null and alternate hypothesis. The F-value seen in the table is then compared to the calculated F-value to determine whether or not to reject the null hypothesis.īelow are the steps where the F-Test formula is used for the null hypothesis that the variances of two populations are equal: It will help determine the F-table value. read more of the numerator and denominator. These nominal values have the freedom to vary, making it easier for users to find the unknown or missing value in a dataset. Subsequently, we must determine the degrees of freedom Degrees Of Freedom Degrees of freedom (df) refers to the number of independent values (variable) in a data sample used to find the missing piece of information (fixed) without violating any constraints imposed in a dynamic system. Then, we need to determine the level of significance under which the test has to carry. 
read more, we need to frame the null and alternative hypotheses. F-test is an essential part of the analysis of variance (ANOVA) model. While F-test in Excel F-test In Excel F-test in excel is a statistical tool that helps us decide whether the variances of two populations having normal distribution are equal or not.
#ANOVA CALCULATOR F HOW TO#
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution link How to Provide Attribution? Article Link to be Hyperlinked F Value = Larger Sample Variance / Smaller Sample Variance = σ 1 2 / σ 2 2







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
